HTML Inline and Block Elements
HTML elements are separated into two major categories: block-level elements and inline elements. These categories define how elements appear and behave around each other on the page.
HTML Inline Elements
Inline elements do not begin a new line and occupy only as much width as they need. The
<span> tag is a good example of an inline element.
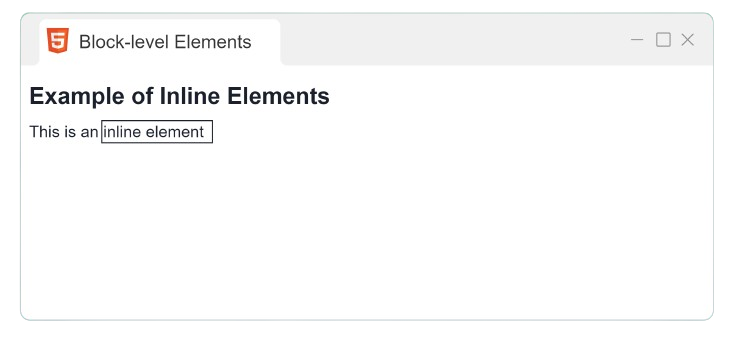
Example:
<p> This is <span style="border:1px solid black;"> inline element </span></p>Output
The inline elements in HTML are as follows:
<a><bdo><cite><i><label><q><small><sup><abbr><big><code><img><map><samp><span><textarea><acronym><br><dfn><input><object><script><strong><time><b><button><em><kbd><output><select><sub><tt>
Block-level Elements
Block-level elements typically begin on a new line and occupy the full available width. The
<p> and
<div> tags are examples of block-level elements.
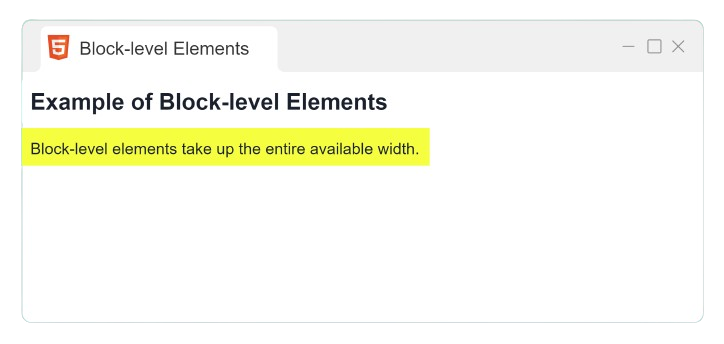
Example:
<p style="border: 1px solid black;"> Block-level elements take up the entire available width. </p>Output
The block-level elements in HTML are as follows:
<address><article><aside><blockquote><canvas><dd><div><dl><dt><fieldset><figcaption><figure><footer><form><header><h1>-<h6><hr><li><main><nav><noscript><ol><ul><pre><p><section><table><video>

